20/01/2024
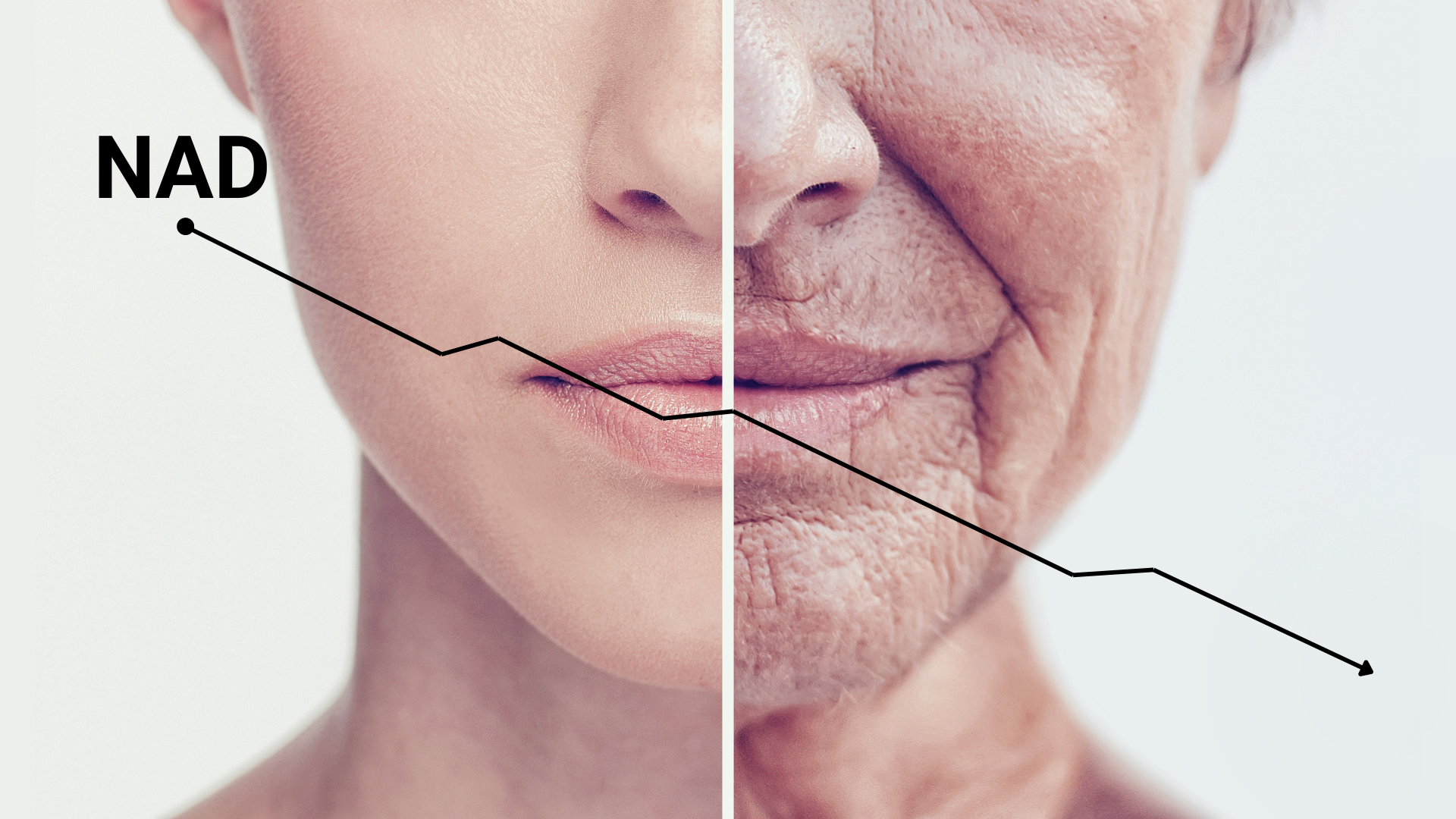
NAD+ can set you on a road of timeless vitality
What is NAD+ and why is it essential? It is a coenzyme, responsible for the functioning of every single cell in the body. It helps with processes including energy production and cellular repair.
As time takes its toll on the body, NAD+ levels plummet (1-3), which could be harmful. The body's levels of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) connect to our health and well-being, through the eight mechanisms below.
Certain special proteins called sirtuins protect our DNA from damage. They act as bodyguards for our DNA. They need NAD+ to do their job.
With passing time, the less and less NAD+ our body has available, like having less power for the bodyguards.
In order to stay healthy and prevent inevitable diseases, we need to make sure we have enough NAD+ our bodies, keeping the bodyguards well-fed and energetic (4).
How NAD+ depletion can impact the body
Although the body carefully regulates the levels of cellular NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), there is a noticeable decrease in the amount of NAD+ inside cells, and a shift in the balance between NAD+ and NADH as people age and experience health issues (5).
These health issues can encompass metabolic disorders, oxidative stress, problems with mitochondrial function, inflammation, and DNA damage.
The signs may surface as (6)
- Tremors
- Depression
- Arterial stiffness
- Circadian rhythm imbalance
- Pro-youth genes turned off
- Restless leg syndrome
- Cellular senescence
- Sarcopenia
- Death
Why does this happen?
These imbalances in NAD+ levels can be explained by a combination of factors:
- There is a decrease in the body's ability to produce NAD+. By age 80, NAD+ levels drop to only 1% to 10% expressed in youth (7,8).
- There is an increase in the activity of enzymes that consume NAD+, leading to a reduced overall NAD+ pool within the cells.
- Essentially, it's like there's less fuel available for the cellular processes that rely on NAD+, which can contribute to various health problems typically associated with occurring later in life (9).
The many ways NAD+ can impact cells
It's like giving your body a helping hand to maintain its health and vitality (20).It helps in the following ways (7)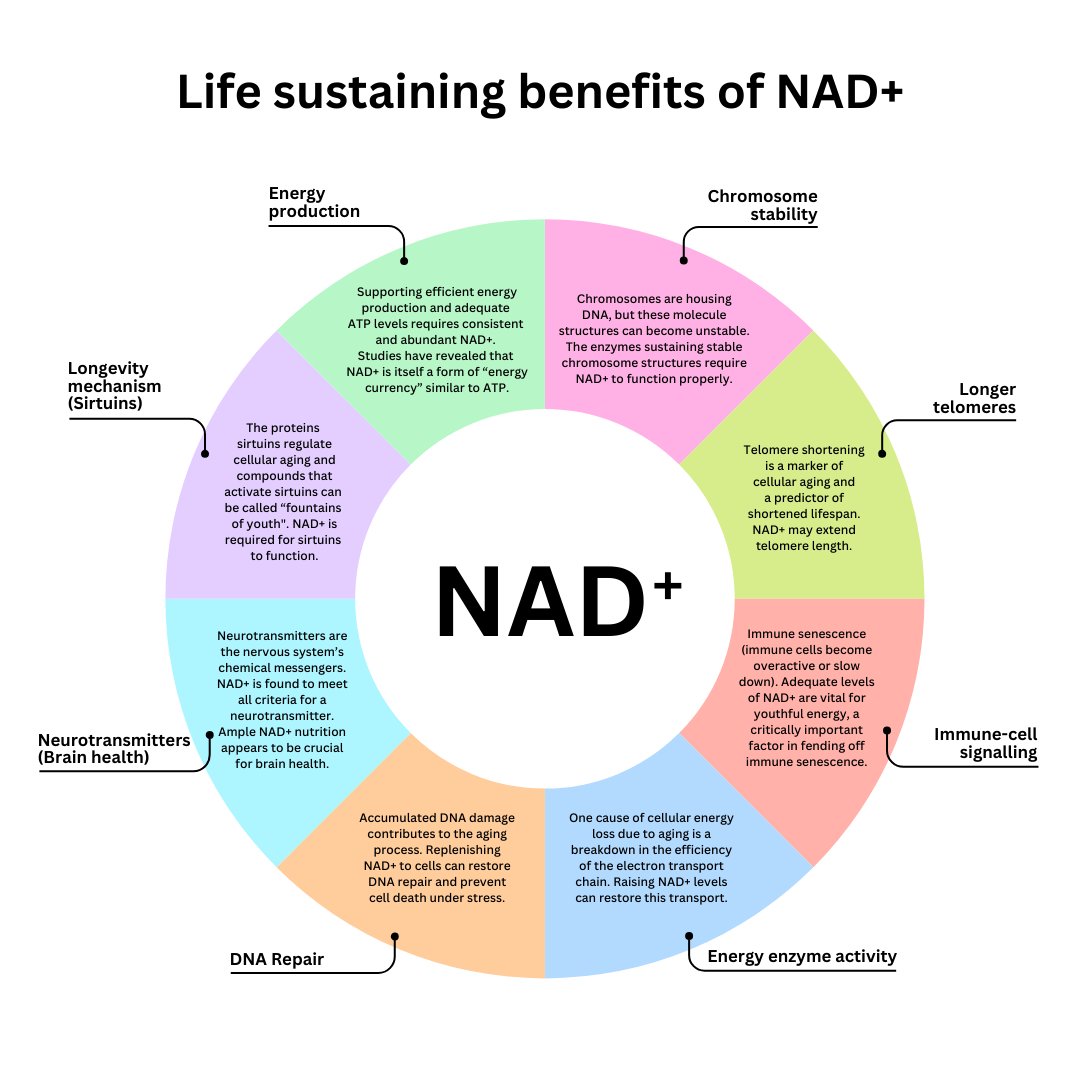
- NAD+ may help maintain longer telomeres, essential for cell renewal and longevity.
- NAD+ supports DNA repair, reducing cellular damage and disease over time.
- Intracellular NAD+ levels influence immune cell function, vital for a robust immune system.
- NAD+ enhances energy production and protects against age-related diseases.
- NAD+ contributes to chromosome stability, reducing the risk of cellular aging and cancer.
- NAD+ functions as a neurotransmitter, supporting brain health.
- Sirtuins, crucial for cellular aging, depend on NAD+ for activation.
- NAD+ is a key player in energy production and overall vitality.
What are telomeres?
Telomeres are like protective caps at the ends of our chromosomes made up of repeated DNA strands. The shortening of telomeres is a sign of cells getting older and can even predict shorter lifespans (10,11).
NAD+ is crucial for the proper functioning of sirtuins, and the sirtuin proteins are responsible for maintaining the length of essential telomeres (7).
Some nutrients like resveratrol might activate sirtuins and potentially contribute to a longer life (16,17). However, recent evidence suggests that sirtuins work best when there's a sufficient supply of NAD+.
By replenishing NAD+ in cells, we could potentially restore the DNA repair process, which gives us hope for slowing down the ageing process and improving our overall longevity (20).
What is the best precursor to NAD+?
B3 vitamins (20), which include nicotinamide riboside (NR), nicotinamide (NAM), and niacin (NA), are essential for our health.
NR is a well-tolerated form of B3 that doesn't cause flushing, a common side effect seen with some other B3 forms in human trials (20).
NR, NA, and NAM are each transformed into NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) through different processes in the body, each with unique characteristics. When we consume NR, our body can convert it into NAD+ through chemical reactions (20).
This is important because NAD+ is a vital molecule for many essential processes in our cells, such as producing energy and repairing cellular damage.
So, by taking nicotinamide riboside as a supplement or through certain foods, you provide your body with a substance that can increase NAD+ levels.
This precursor to NAD+ can offer several health benefits, including potentially raising your vitality and improving the overall functioning of your cells.

Why NAD+ and not NAD?
NAD+ and NAD are both molecules that play important roles in the body. NAD is a collective term for all the different forms NAD takes throughout the various chemical processes it takes in our body. NAD+ is the biologically active form of NAD that has catalytic properties (20,21).
When NAD+ receives electrons, it is transformed into a reduced form called NADH, which is also known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H) (21).
The difference between NAD and NAD+ is that NAD+ is a molecule that has catalytic properties and is biologically active, while NAD is a collective term for all the different forms NAD takes throughout the various chemical processes it takes in our body (21).
NAD+ carries the electrons of a hydride from one region of a cell to another. Without molecules like NAD+, electrons could hardly make it to their proper destination (21).
NAD+ and NADH are important molecules in the context of metabolizing food for energy.
Without the electron carrying capacity of NAD+, our cells wouldn’t be able to metabolize food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy used by our cells to keep us alive (20-25).
Taking resveratrol together with NAD+ can help
Resveratrol and nicotinamide riboside can boost each other's benefits.
Resveratrol promotes longevity by activating proteins called sirtuins. For sirtuins to function, they require the coenzyme NAD+.
One of the key ways, resveratrol works is to activate life-extending sirtuins (26-29).
Because sirtuins require NAD+ to function, resveratrol's benefits cannot be maximized without also ensuring ample NAD+ levels.
NAD+ Cell Regenerator™ and Resveratrol Elite™ combines 300 mg of NIAGEN® nicotinamide riboside with an ultra-bioavailable trans-resveratrol (as well as bioavailability-enhanced forms of the phytonutrients quercetin and fisetin) to fight general fatigue and promote longevity with every dose by supporting heart, mind & cell health.
NIAGEN® is a patented supplement that elevates NAD+ levels through the use of nicotinamide riboside.
Resveratrol, quercetin, and fisetin have demonstrated their ability to enhance various aspects of health, including:
- Mechanisms related to longevity
- Heart and immune system well-being
- The removal of senescent cells
This supplement combines highly absorbable versions of all four nutrients, creating an unparalleled formula designed to enhance energy, vitality, and fortify against the effects of cellular aging (30-33).
Read more blog posts about NAD+
References
- Johnson S, Imai SI. NAD (+) biosynthesis, aging, and disease. F1000Res. 2018;7:132.
- Imai S, Guarente L. NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;24(8):464-71.
- Zhou CC, Yang X, Hua X, et al. Hepatic NAD(+) deficiency as a therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in ageing. Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;173(15):2352-68.
- Rajman L, Chwalek K, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence. Cell Metab. 2018 Mar 6;27(3):529-47.
- https://pro.truniagen.com/Documents/HCP/EducationAndResources/Tru-Niagen-Monograph-10.20.pdf
- https://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2019/2/nad-restoration
- https://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2018/2/anti-aging-effects-of-nad
- Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/life-expectancy.htm. Accessed November 15, 2017.
- Imai SI, Guarente L. It takes two to tango: NAD+ and sirtuins in aging/longevity control. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2016;2:16017.
- Gopalakrishnan S, Cheung NK, Yip BW, et al. Medaka fish exhibits longevity gender gap, a natural drop in estrogen and telomere shortening during aging: a unique model for studying sex-dependent longevity. Front Zool. 2013;10(1):78
- Heidinger BJ, Blount JD, Boner W, et al. Telomere length in early life predicts lifespan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(5):1743-8
- Carulli L, Anzivino C, Baldelli E, et al. Telomere length elongation after weight loss intervention in obese adults. Mol Genet Metab. 2016;118(2):138-42.
- Honka MJ, Bucci M, Andersson J, et al. Resistance training enhances insulin suppression of endogenous glucose production in elderly women. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;120(6):633-9.
- Sjogren P, Fisher R, Kallings L, et al. Stand up for health--avoiding sedentary behaviour might lengthen your telomeres: secondary outcomes from a physical activity RCT in older people. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(19):1407-9.
- Bonkowski MS, Sinclair DA. Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(11):679-90.
- Rowlands BD, Lau CL, Ryall JG, et al. Silent information regulator 1 modulator resveratrol increases brain lactate production and inhibits mitochondrial metabolism, whereas SRT1720 increases oxidative metabolism. J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(7):1147-56.
- Hung CH, Chan SH, Chu PM, et al. Quercetin is a potent anti-atherosclerotic compound by activation of SIRT1 signaling under oxLDL stimulation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59(10):1905-17.
- Xiao N, Mei F, Sun Y, et al. Quercetin, luteolin, and epigallocatechin gallate promote glucose disposal in adipocytes with regulation of AMP-activated kinase and/or sirtuin 1 activity. Planta Med. 2014;80(12):993-1000.
- Oka S, Hsu CP, Sadoshima J. Regulation of cell survival and death by pyridine nucleotides. Circ Res. 2012;111(5):611-27.
- https://www.truniagen.com/blog/science-101/what-is-nad/#:~:text=Taking%20Vitamin%20B3%20Is%20the%20Best%20Way%20to%20Boost%20NAD%2B%20Levels&text=B3%20vitamins%20are%20precursors%20used,in%20multivitamins%20and%20breakfast%20cereals.
- https://www.truniagen.com/blog/science-101/nad-vs-nad-vs-nadh-whats-the-difference/
- https://strongcell.com/blogs/articles/nad-nad-and-nadh-the-differences-explained
- https://driphydration.com/blog/difference-between-the-types-of-nad/
- Available at: https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/cell-energy-and-cell-functions-14024533. Accessed November 15, 2017.
- https://www.truniagen.com/science/
- Moon J, Kim HR, Shin MG. Rejuvenating Aged Hematopoietic Stem Cells Through Improvement of Mitochondrial Function. Ann Lab Med.2018Sep;38(5):395-401.
- Yang Q, Cong L, Wang Y, et al. Increasing ovarian NAD(+) levels improve mitochondrial functions and reverse ovarian aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020Aug 20;156:1-10.
- Xie X, Gao Y, Zeng M, et al. Nicotinamide ribose ameliorates cognitive impairment of aged and Alzheimer's disease model mice. Metab Brain Dis. 2019Feb;34(1):353-66.
- Fang EF. Mitophagy and NAD(+) inhibit Alzheimer disease. Autophagy. 2019Jun;15(6):1112-4.
- Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(6):1258-1277.
- Phytother Res. 2022
- Clin Nutr. 2021;40(3):820-829.
- Nat Commun. 2016;7:12948.